As the dog obesity epidemic steadily rises, understanding the pivotal role of diet in managing a dog's weight has become increasingly crucial. This article aims to dissect the escalating prevalence of obesity in dogs, highlighting the profound impact of dietary choices on their overall health. Exploring the importance of tailored nutrition and its influence on weight management, it navigates through strategies, nutritional guidelines, and lifestyle adjustments. By examining the intricate link between diet and dog weight, this piece offers insights and practical solutions for pet owners striving to address this trend.
10 Simple Ways to Understand Dog Obesity
Quick Pointers
1. Dog obesity is an excessive buildup of body fat.
2. It's a major health issue for dogs.
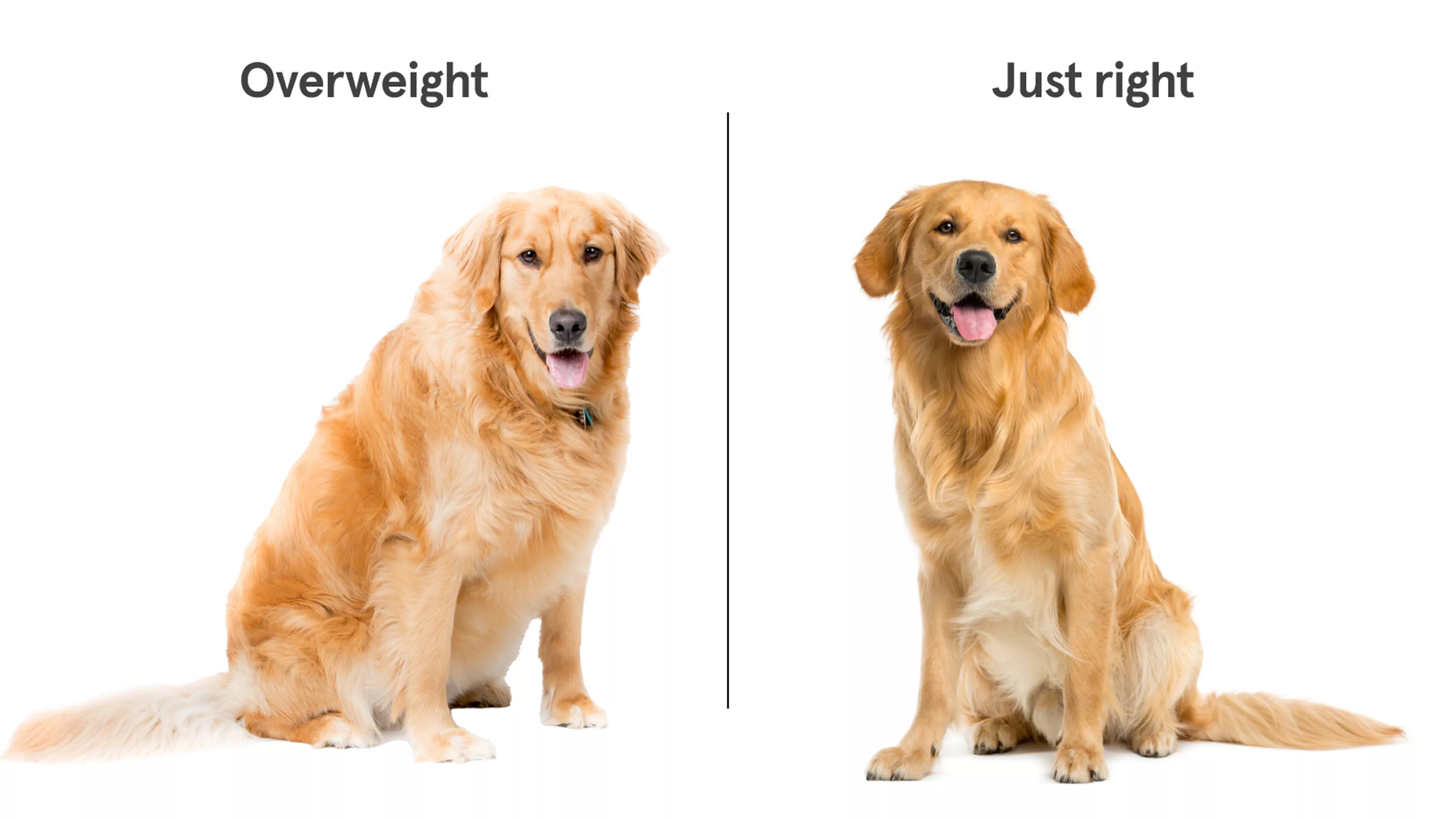
3. Obesity is measured using a body condition score (BCS).
4. BCS checks for a visible waist, feeling the ribs, and abdominal shape.
5. A BCS of 8 or 9 out of 9 means obesity.
6. Obesity is when ribs are covered by fat and the waist isn't visible.
7. Dogs are obese if they weigh 15-20% above their ideal weight.
8. It's caused by eating too many calories compared to what they burn off.
9. Leads to increased risk of joint issues, diabetes, and heart disease.
10. Management includes diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes for a healthier weight.
Factors Contributing to Dog Obesity
Several factors contribute to obesity in dogs, as highlighted by studies available in the National Library of Medicine:
1. Overfeeding and Diet Composition: Excessive calorie intake, whether through overfeeding or high-calorie diets, significantly contributes to obesity. Poor diet choices, such as high-fat or high-carbohydrate diets, can also play a role.
2. Lack of Physical Activity: Inadequate exercise or a sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain in dogs. Reduced activity levels and excess calorie intake result in energy imbalance, contributing to obesity.
3. Breed Predisposition and Genetics: Certain breeds are more susceptible to obesity due to genetic factors. Breeds like Labrador Retrievers, Beagles, and Cocker Spaniels are more prone to weight gain.
4. Age and Neutering: Age-related metabolic changes can influence weight gain in older dogs. Neutering can also impact metabolism, potentially leading to weight gain if calorie intake isn't adjusted accordingly.
5. Owner Behaviour and Feeding Practices: Feeding habits, including free-choice feeding or excessive treat-giving, can contribute to obesity. Additionally, a lack of awareness or misinterpretation of a dog's body condition can lead to overfeeding.
6. Medical Conditions and Medications: Underlying conditions such as hypothyroidism or certain medications can contribute to dog weight gain, requiring careful monitoring and management.
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and manage dog obesity, emphasizing balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and attentive feeding practices.
Health Implications of Dog Obesity Across Age Groups

Dog obesity affects dogs of all ages, exerting varying health implications. From skeletal growth issues in puppies to exacerbated age-related conditions in seniors, it spans joint stress, cardiovascular strain, and immunity compromise. Understanding these age-specific impacts is crucial for effective preventive measures and tailored weight management strategies.
Puppies:
Growth Abnormalities: Obesity during puppyhood can lead to skeletal development issues and improper growth patterns.
Joint Stress: Excess weight can strain developing joints, potentially causing long-term common problems like hip dysplasia.
Adult Dogs:
Orthopaedic Issues: Increased risk of arthritis, joint pain, and ligament injuries due to added stress on joints.
Cardiovascular Problems: Obesity can lead to heart disease and hypertension, impacting the cardiovascular system.
Respiratory Complications: Difficulty breathing and decreased stamina are common due to the strain on the respiratory system.
Senior Dogs:
Exacerbated Age-Related Conditions: Obesity can worsen age-related health issues like arthritis and decrease mobility.
Decreased Immunity: Obesity can compromise the immune system, making senior dogs more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Breeds Vulnarable to Obesity
Labrador Retrievers: Known for their love of food, Labs can quickly gain weight if their diet and exercise aren't well-regulated.
Beagles: These dogs have a strong food drive, making them prone to overeating if portion control isn’t strictly maintained.
Cocker Spaniels: They are inclined to weight gain due to their tendency to be less active and potential genetic predisposition.
Dachshunds: Their elongated body structure can strain the spine and joints if carrying excess weight.
Basset Hounds: With their low activity levels and a propensity for overeating, Basset Hounds are at risk for obesity-related health issues.
Shih Tzus: These small dogs can gain weight quickly if their diet isn't carefully managed due to their lower exercise needs.
Managing the weight of these breeds requires a balanced diet, portion control, regular exercise, and close monitoring of their body condition to prevent obesity-related health complications.
Dietary Factors Influencing Dog Obesity
Role of caloric intake in weight management
Calorie intake plays a pivotal role in a dog's weight gain, directly impacting their energy balance. When dogs consume more calories than they expend through daily activities and bodily functions, the excess energy is stored as fat, leading to weight gain over time.
Adipose tissue holds the surplus calories from food that the body doesn't use for fuel, increasing body fat. Controlling calorie intake is essential for maintaining a healthy weight in dogs. It requires a balanced diet aligned with their activity level and nutritional needs.
Monitoring portion sizes and choosing nutrient-dense, appropriate-calorie food is vital to managing a dog's weight and overall health.
Impact of macronutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) on dog weight
The impact of macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—on dog weight is significant and varies based on several factors:
Proteins: Essential for muscle growth and repair, proteins also aid in weight management. A high-protein diet can support dog weight loss by promoting satiety and preserving lean muscle mass during calorie restriction.
Fats: While fats are a dense energy source, excessive intake can lead to weight gain. However, moderate amounts of healthy fats are crucial for nutrient absorption, energy, and overall health. Regulating fat intake is essential in managing overall caloric intake and weight control.
Carbohydrates: The role of carbohydrates in dog weight management is debated. Complex carbohydrates from sources like whole grains and vegetables provide energy and fibre, aiding digestion. However, excessive simple carbohydrates can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with activity levels.
The ideal macronutrient composition for a dog's diet depends on age, activity level, and specific health needs. Balanced proportions of these macronutrients are crucial to maintaining a healthy weight in dogs while ensuring adequate nutrition for optimal health.
Influence of feeding frequency and portion control
Feeding frequency and portion control significantly influence dog dog:
-
Feeding Frequency:
Frequent feeding can lead to overconsumption if portion sizes aren't regulated. Multiple meals a day might suit some dogs, but monitoring total daily intake is essential.
Irregular feeding patterns or free-choice feeding where food is constantly available can lead to weight gain as dogs might eat more than needed.
-
Portion Control:
Controlling portion sizes is crucial in managing weight. Even with nutritious food, overfeeding contributes to excess calorie intake and weight gain.
Measuring food accurately based on a dog's size, activity level, and dietary requirements helps prevent overconsumption.
Balancing feeding frequency and portion control is vital. Scheduled portion-controlled meals can regulate calorie intake, preventing obesity.
Effects of treats, table scraps, and human food on obesity rates
Including treats, table scraps, and human food in a dog's diet significantly impacts obesity rates.
Similarly, while occasionally enjoyed by dogs, table scraps and human food tend to be rich in fats, salts, and sugars, leading to excess weight gain when incorporated regularly.
These additions to a dog's diet can disrupt their balanced nutrition, causing an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure, thereby elevating the risk of obesity. Strict control over the quantity and quality of treats, table scraps, and human food offered to dogs is crucial to prevent the development of obesity and maintain their overall health.
Treats, often high in calories and lacking in nutritional balance, can contribute substantially to a dog's daily calorie intake if not moderated.
Choosing the Right Diet for Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight in dogs involves more than portion control; it requires a diet balanced with the right nutrients. Proper nutrition is crucial for dogs' weight management and overall well-being.
Importance of Balanced Nutrition
Achieving and sustaining a healthy weight in dogs isn't just about reducing portions; it's about ensuring they receive essential nutrients. A balanced diet supports overall health, aiding in weight management by keeping dogs satisfied while meeting their nutritional requirements. Essential nutrients like proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals are pivotal in a dog's well-being and weight regulation.
Understanding Dietary Requirements
Different life stages and breeds have distinct nutritional needs. Puppies need diets rich in protein and specific nutrients to support growth. At the same time, seniors may require fewer calories but higher-quality proteins and joint-supporting supplements. Understanding these nuances is vital in crafting diets that cater to their age, size, activity level, and health status.
Evaluation of Commercial Dog Foods
Reading and comprehending dog food labels are paramount. Look for high-quality protein sources like meat or fish listed as the primary ingredients, with minimal filler content. Avoid foods with excessive additives, artificial flavours, or preservatives. Opt for reputable brands like Perfekt that meet stringent nutritional standards set by regulatory bodies.
Consideration of Specialised Diets
Specialized diets designed explicitly for weight management offer tailored solutions. These diets often have controlled calorie content, balanced nutrients, and added components like fibre to promote satiety. Consultation with a veterinarian can aid in selecting the correct specialized diet that aligns with a dog's weight management goals and health conditions.
Further reading:
Conclusion
In the quest for effective dog weight management, it's crucial to recap the essentials: understanding dietary factors, implementing portion control, incorporating exercise, and addressing behavioural aspects. However, the cornerstone remains a balanced diet and lifestyle tailored to a dog's needs. Opting for high-quality, ready-to-eat Perfekt pet food ensures optimal nutrition without compromising taste or quality. Seek professional guidance, partner with vets for personalized plans, and embrace various flavours from Perfekt to secure their health and happiness. Let's empower our pets toward a healthier tomorrow!
Obesity and Health: Dog obesity is a growing issue, exacerbated by factors such as overfeeding and sedentary lifestyles, affecting health across all ages.
Dietary Management: Effective weight control in dogs necessitates balanced nutrition tailored to individual life stages, breeds, and health conditions.
Choosing Food: High quality, lower caloric density food is a great choice.